Cartpole using Q-learning
Reinforcement Learning Implementation for Cartpole Control
📋 Project Overview
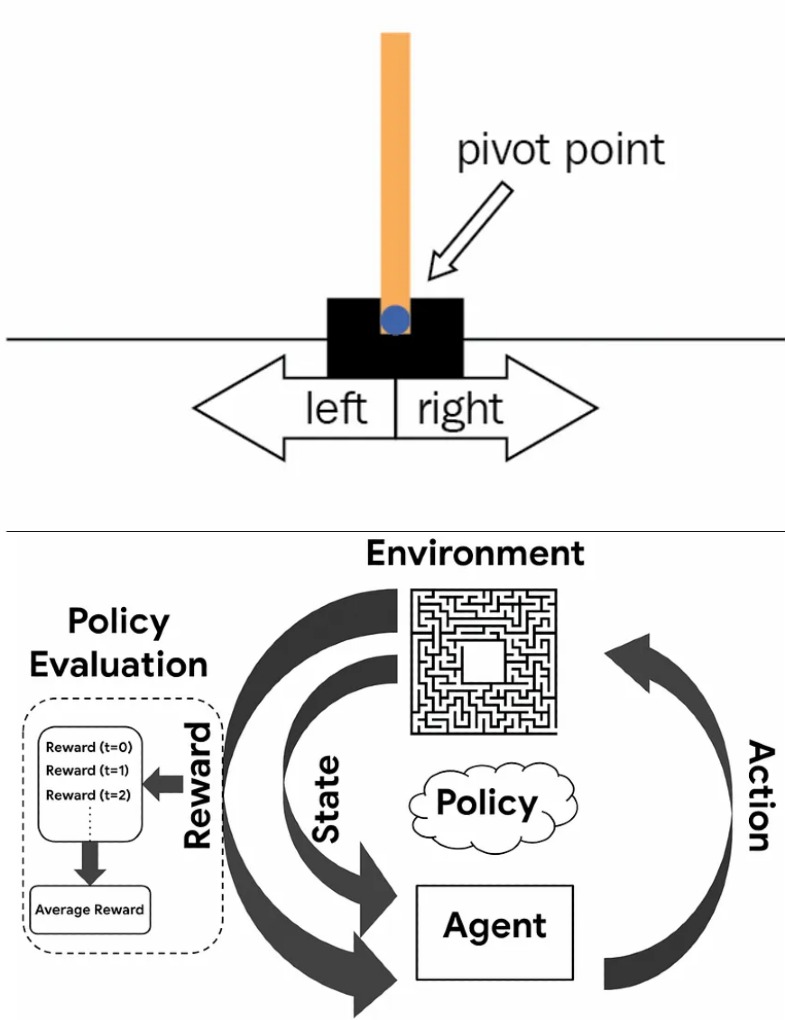
The Cartpole Q-learning project demonstrates the application of reinforcement learning to solve a classic control problem. The cartpole (inverted pendulum) is a fundamental benchmark in control theory and reinforcement learning, where an agent must learn to balance a pole on a moving cart by applying forces left or right.
This project implements Q-learning, a value-based reinforcement learning algorithm, to train an agent that can successfully balance the pole. The implementation includes state discretization, Q-table management, exploration-exploitation strategies, and performance visualization.
💡 Problem Statement
The cartpole problem presents several learning challenges:
- Continuous State Space: Cart position, velocity, pole angle, and angular velocity are continuous
- Discrete Actions: Only two actions available: push left or push right
- Delayed Rewards: Agent receives reward only when pole stays balanced
- Exploration vs Exploitation: Balancing between trying new actions and using learned knowledge
- State Discretization: Converting continuous states to discrete Q-table indices
- Convergence: Ensuring the algorithm learns an optimal policy
⚡ Solution Approach
The project implements Q-learning with the following components:
- State Discretization: Binning continuous state variables into discrete buckets
- Q-Table: Multi-dimensional table storing Q-values for state-action pairs
- Epsilon-Greedy Policy: Exploration strategy with decaying epsilon
- Q-Learning Update: Temporal difference learning to update Q-values
- Reward Shaping: Designing reward function for effective learning
- Episode Management: Training over multiple episodes with reset conditions
🛠️ Technical Implementation
Q-Learning Algorithm
- State Space: [cart_position, cart_velocity, pole_angle, pole_angular_velocity]
- Action Space: {0: push_left, 1: push_right}
- Q-Table Initialization: Random or zero initialization
- Q-Update Rule: Q(s,a) = Q(s,a) + α[r + γ*max(Q(s',a')) - Q(s,a)]
- Learning Rate (α): Controls update magnitude
- Discount Factor (γ): Values future rewards
- Epsilon Decay: Gradually reduces exploration over time
Implementation Details
- Environment: OpenAI Gym CartPole-v1 or custom implementation
- State Discretization: Uniform or adaptive binning strategies
- Reward Function: +1 for each step pole remains balanced
- Episode Termination: When pole falls or max steps reached
- Training Loop: Multiple episodes with Q-table updates
- Evaluation: Testing learned policy without exploration
- Visualization: Plotting learning curves and episode rewards
🏆 Key Achievements
- ● Successfully learned to balance pole for extended periods
- ● Converged to stable policy within reasonable training time
- ● Demonstrated understanding of Q-learning fundamentals
- ● Effective state discretization strategy
- ● Comprehensive visualization of learning process
💡 Challenges Overcome
- ● Choosing appropriate state discretization granularity
- ● Balancing exploration and exploitation rates
- ● Tuning hyperparameters (learning rate, discount factor)
- ● Managing Q-table memory for high-dimensional states
- ● Ensuring convergence to optimal policy
📚 Key Learnings
- Reinforcement Learning: Understanding the fundamentals of RL and Q-learning
- Markov Decision Process: Modeling problems as MDPs with states, actions, and rewards
- Value Functions: Learning action-value functions (Q-functions)
- Exploration Strategies: Epsilon-greedy and other exploration techniques
- State Discretization: Converting continuous to discrete state spaces
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Impact of learning rate, discount factor, and epsilon
🚀 Future Enhancements
- Deep Q-Network (DQN) for handling continuous states without discretization
- Double DQN and Dueling DQN for improved stability and performance
- Prioritized Experience Replay for more efficient learning
- Multi-agent reinforcement learning for competitive scenarios
- Transfer learning to adapt to variations of the cartpole problem
- Policy gradient methods (REINFORCE, Actor-Critic) for comparison
- Real-world hardware implementation on physical cartpole system