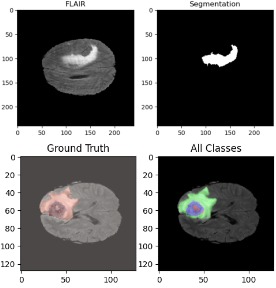
Brain Tumor Segmentation
Medical Image Segmentation using W-Net and Deep Neural Networks
📋 Project Overview
Brain tumor segmentation is a critical task in medical imaging that involves identifying and delineating tumor regions in brain MRI scans. This project implements a state-of-the-art W-Net architecture for automated brain tumor segmentation, enabling accurate detection and classification of different tumor regions including edema, enhancing tumor, and necrotic/non-enhancing tumor core.
The project addresses the challenge of precise tumor boundary detection, which is essential for treatment planning, surgical navigation, and monitoring tumor progression. By leveraging deep learning techniques, we achieve high-accuracy segmentation that can assist radiologists in diagnosis and treatment planning.
💡 Problem Statement
Manual segmentation of brain tumors from MRI scans is time-consuming, subjective, and requires extensive expertise. The complexity increases when dealing with:
- Multi-modal imaging: Different MRI sequences (T1, T1CE, T2, FLAIR) provide complementary information
- Class imbalance: Tumor regions are significantly smaller than healthy brain tissue
- Boundary ambiguity: Tumor edges can be unclear and vary in intensity
- Heterogeneous appearance: Different tumor types and regions have varying characteristics
- Noise and artifacts: Medical images often contain noise that affects segmentation accuracy
⚡ Solution Approach
The project implements a W-Net architecture, which consists of two U-Nets connected in series:
- Encoder-Decoder Architecture: First U-Net performs initial segmentation, capturing multi-scale features
- Refinement Network: Second U-Net refines the segmentation output, improving boundary accuracy
- Multi-modal Fusion: Integrates information from T1, T1CE, T2, and FLAIR sequences
- Attention Mechanisms: Focuses on relevant regions while suppressing background noise
- Dice Loss Optimization: Addresses class imbalance by focusing on overlapping regions
🛠️ Technical Implementation
Architecture Details
- W-Net Structure: Two cascaded U-Nets with skip connections for feature preservation
- Input Processing: Multi-channel input combining T1, T1CE, T2, and FLAIR sequences
- Feature Extraction: 3D convolutions to capture spatial context in volumetric data
- Downsampling: Max pooling and strided convolutions for multi-scale feature learning
- Upsampling: Transposed convolutions and bilinear interpolation for precise reconstruction
- Skip Connections: Concatenation of encoder and decoder features at corresponding levels
Training Strategy
- Data Augmentation: Rotation, flipping, intensity scaling, and elastic deformations
- Loss Function: Combined Dice loss and cross-entropy for balanced optimization
- Optimization: Adam optimizer with learning rate scheduling
- Validation: K-fold cross-validation on BraTS dataset
- Post-processing: Connected component analysis and morphological operations
🏆 Key Achievements
- ● High Dice coefficient scores for all tumor sub-regions
- ● Accurate boundary detection for surgical planning
- ● Robust performance across different tumor types and sizes
- ● Efficient inference time for clinical applications
- ● Multi-modal fusion for comprehensive tumor analysis
💡 Challenges Overcome
- ● Handling class imbalance between tumor and background pixels
- ● Managing memory constraints with 3D volumetric data
- ● Fusing multi-modal information effectively
- ● Dealing with ambiguous tumor boundaries
- ● Optimizing for both accuracy and inference speed
📚 Key Learnings
- Medical Image Processing: Understanding the nuances of MRI sequences and their clinical significance
- Deep Learning for Healthcare: Importance of interpretability and reliability in medical AI applications
- Architecture Design: How cascaded networks can improve segmentation accuracy through refinement
- Loss Function Design: Balancing different loss components for optimal performance on imbalanced datasets
- Data Augmentation: Domain-specific augmentation techniques for medical imaging
- Evaluation Metrics: Understanding Dice coefficient, Hausdorff distance, and sensitivity/specificity in medical context
🚀 Future Enhancements
- Integration of transformer-based architectures for better long-range dependencies
- Uncertainty quantification to provide confidence scores for segmentation
- 3D attention mechanisms for improved spatial context understanding
- Federated learning for privacy-preserving multi-institutional training
- Real-time segmentation for intraoperative guidance
- Multi-task learning combining segmentation with tumor grading
- Explainable AI features for clinical interpretability